Made of clay or ceramic. Applied with fire or vacuum suction
Features
Similar to glass cups, but heavier. Fragile, less commonly used today
Best For
Traditional clinics, cultural or historic treatments
Ceramic or Porcelain Cups

Precautions and Contraindications
-
Avoid cupping over:
-
Open wounds, burns, skin infections
-
Varicose veins
-
Abdomen and lower back in pregnancy
-
Very thin, elderly, or Yin-deficient patients (use with care)
-
-
Skin markings ("cupping marks"):
-
Not bruises; they are due to stagnation being drawn to the surface.
-
Usually fade in 3–7 days
-
Darker marks indicate deeper stagnation.
-

Types of Cupping Techniques
Dry cupping
Suction only (no bleeding)
A cup is applied to the skin using fire or a suction pump and left in place for 5–15 minutes.
A cup is applied to the skin using fire or a suction pump and left in place for 5–15 minutes.
Muscle tension, back pain, Wind-Cold invasion
Wet cupping (bloodletting cupping)
Scarification followed by cupping to draw blood
The skin is pricked with a lancet or plum blossom needle before cupping to draw out a small amount of blood under suction.
Clears Heat, reduces stasis, detoxifies Blood, expels toxic Heat or stagnation.
Toxin removal, Heat, Blood stasis
Flash cupping
Cups quickly applied and removed repeatedly
Cups are quickly applied and removed repeatedly (usually 5–10 times) in the same area.
Stimulates circulation without prolonged suction.
Stimulates surface, useful for colds or early Wind invasion
Moving cupping
Cup is moved over oiled skin
A cup is applied to oiled skin and moved along muscle lines or meridians. Use massage oil to reduce friction.
Combines cupping with massage to release myofascial tension and unblock meridians.
Muscular pain, myofascial release
Retention cupping
Cups remain on the skin for 5–15 minutes
Deep stagnation, Cold, chronic tension
Fire cupping
Fire inserted briefly to create suction in glass cup before application
A flame is quickly inserted into the glass cup to remove oxygen, then the cup is applied to create vacuum suction.
Traditional form of dry cupping with strong suction.
Traditional method; effective but requires skill
Herbal Cupping / Steaming cupping
The inside of the cup is filled or infused with steaming herbal substances before application.
Enhances cupping with herbal actions (e.g., warming, anti-inflammatory).
Cold-Damp bi syndrome, Dermatological conditions, Postpartum recovery
Needle Cupping (Acupuncture + Cupping)
Acupuncture needles are inserted, and cups are placed over the area to enhance the treatment.
Combines the effects of point stimulation and local suction to intensify Qi movement.
Deep musculoskeletal pain, Stubborn stagnation, Chronic Bi syndrome
Empty / Weak Cupping (Low Suction)
Very light suction applied for a short duration.
Gentle stimulation without strong stagnation release.
Elderly or frail patients, Children, Yin-deficient or weakened constitutions
Made of soft, flexible medical-grade silicone. Applied by squeezing the cup to create vacuum.
Features
Easy to apply and remove. Comfortable for the patient. No fire or pump needed. Easy to use in moving cupping
Best For
Facial cupping, massage cupping, sensitive patients. Ideal for muscle tension, cosmetic therapy, self-care
Soft, flexible
Silicone Cups
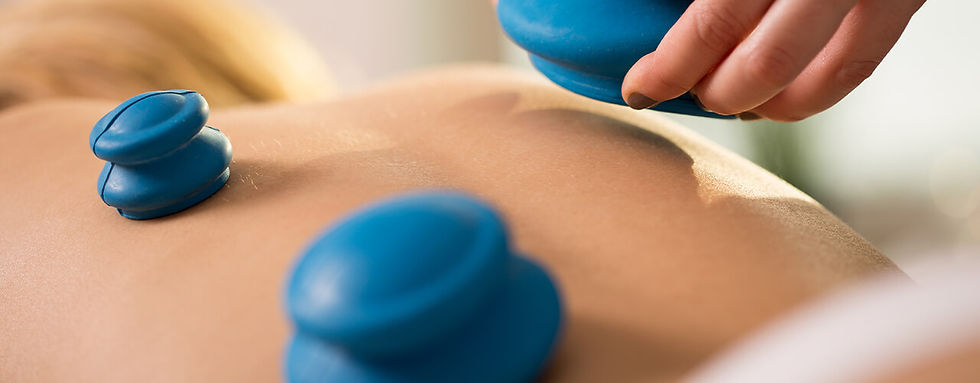

Hollow bamboo segments, open at one end. Heated before application to create suction
Features
Traditional, rustic feel. Porous — difficult to sterilize, absorb fluids
Best For
Traditional wet cupping or fire cupping in rustic TCM practice. Often used with herbs placed inside (herbal steaming effect)
Bamboo Cups
Made of thick glass, often round with a smooth rim. Traditionally used with fire cupping: a flame is inserted into the cup to heat the air and create suction when applied to the skin
Features
Transparent → allows easy observation of skin reaction. Easy to sterilize. Require careful handling due to breakability and fire.
Best For
Retention cupping, wet cupping (bloodletting). Treating back pain, stagnation, cold invasion
Most common, used with flame
Glass cups
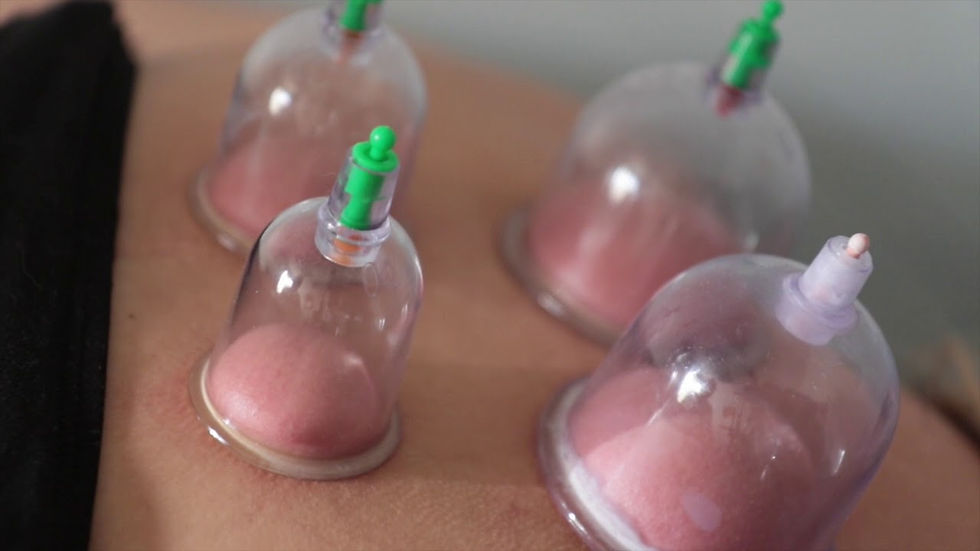


Made of durable plastic. Use a hand-held pump to create suction — no fire involved
Features
Safe, no fire required. Adjustable suction level. Often used in modern clinics or home use
Best For
Beginners, general clinical use, dry cupping, flash cupping
Use hand-pump suction
Plastic Cups

What is Cupping?
Cupping therapy is a traditional treatment method used in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) and other healing systems to promote circulation of Qi and Blood, disperse stagnation, and expel Wind, Cold, and Dampness from the body. It involves placing cups on the skin to create suction, drawing the skin and superficial muscles upward into the cup. In TCM, cupping is considered a method of external treatment that complements acupuncture and moxibustion. It is used for both internal and external disorders, especially those caused by stagnation, Cold invasion, or Qi and Blood obstruction. According to TCM principles, cupping:
-
Unblocks meridians and collaterals.
-
Moves Qi and Blood in areas of stagnation.
-
Draws out external pathogens (Wind, Cold, Damp)
-
Reduces swelling and relieves pain.
-
Promotes detoxification through the pores.
