GANs consist of two competing neural networks—a generator and a discriminator—that produce new, realistic data. In TCM, GANs are used to generate customised herbal prescriptions by learning from large datasets of classical and clinical prescriptions, supporting the development of novel treatment plans tailored to individual patient needs.
Generative Adversarial Networks
(GANs)


Hybrid-scale graph contrastive learning is especially well-suited for TCM's holistic diagnostic framework, which integrates physical and psychological health indicators. This model uncovers latent patterns in TCM formulations by analysing the relationships among multiple herbs, diseases, and syndromes, aiding the discovery of clinically relevant herbal combinations and improving the understanding of TCM logic and formulation strategies.
Hybrid-Scale Graph Contrastive Learning
GATS apply attention mechanisms to graph-structured data, allowing AI to focus on the most relevant features when analysing herb-compound interactions. In TCM, GATs recommend herbs based on their therapeutic relationships and synergistic effects, enabling more precise and personalised herbal prescriptions.
Graph Attention Networks
(GATs)
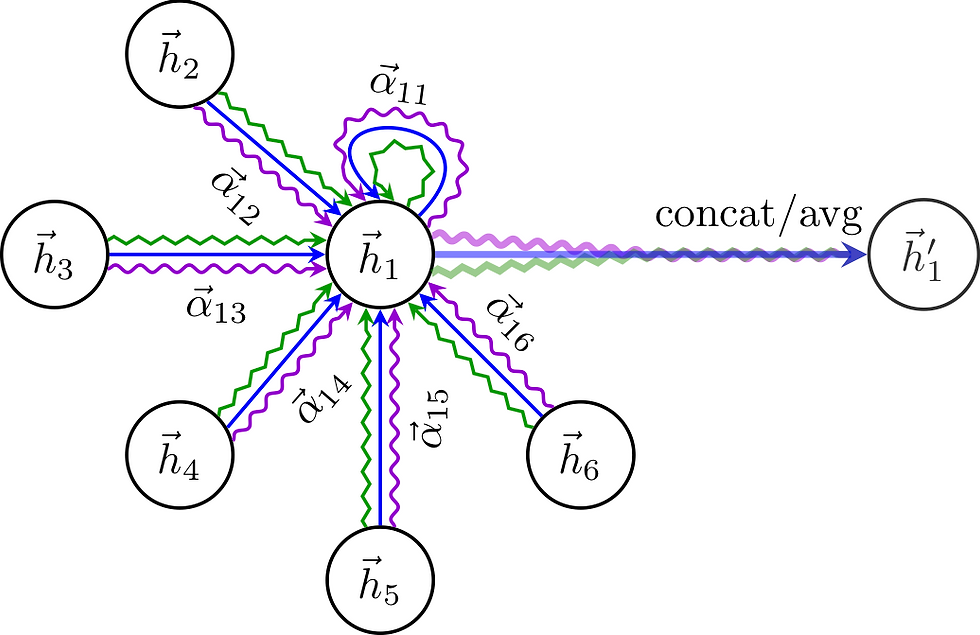

Representation learning is fundamental to building TCM knowledge graphs. It transforms complex clinical and pharmacological data into structured, machine-readable formats, facilitating improved information retrieval, pattern recognition, and the construction of intelligent decision-support systems in TCM.
Representation Learning

Innovative AI Models and Techniques in TCM Research
A new generation of artificial intelligence models is reshaping the landscape of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) by enabling more accurate, personalised, and evidence-informed approaches to diagnosis, treatment, and research. These technologies support a shift from intuition-based practice to data-enhanced decision-making, while respecting the holistic principles that underpin TCM. A range of AI models and techniques are enacted in TCM research. These include.
These advanced technologies collectively facilitate a paradigm shift in Traditional Chinese Medicine—from empirical, experience-based practices toward more standardised, data-driven, and personalised approaches. By aligning ancient wisdom with modern scientific standards, AI empowers TCM to become more precise, reproducible, and adaptable to contemporary clinical and research environments.
Transformer-Based Models and Deep Cross Neural Networks
Handle large patient datasets to generate tailored treatment strategies and optimise prescription planning—pioneering more precise and responsive inpatient care in TCM.
Service Personalised Medicine and Clinical Decision Support
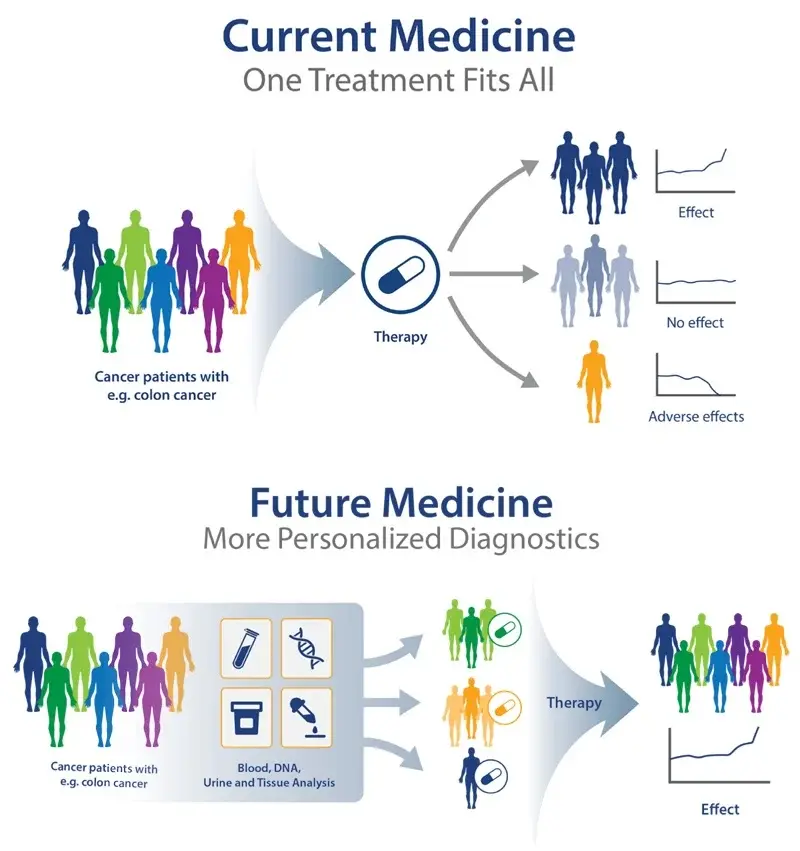
Graph Neural Networks (GNNs)
Ideal for modelling the non-linear, relational structure of TCM data (e.g., herb-compound-disease networks). GNNs enhance auxiliary diagnosis and facilitate the identification of novel therapeutic pathways.
Graph Attention Networks (GATs)
Enhance herb recommendation systems by analysing intricate chemical and pharmacological relationships among herbal components.
Hybrid-Scale Graph Contrastive Learning
Applied in formula discovery, this method detects underlying regularities in herbal combinations, supporting the rational design of effective formulas.
Network and Graph-Based Models

Deep Learning and Imaging
Deep Learning and Imaging
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)
Recognising visual patterns in molecular images can improve the chemical structure analysis of herbal compounds, facilitating drug discovery and predicting compound function.
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
Used to generate personalised TCM prescriptions by learning from traditional prescription patterns and chemical data.

Applications of AI in TCM
AI technologies are revolutionising Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) by offering sophisticated tools for data analysis, diagnostic support, treatment personalisation, and knowledge discovery. Integrating cutting-edge models—such as deep learning, graph-based networks, and natural language processing—enables researchers and clinicians to uncover complex relationships within TCM systems and enhance clinical efficacy.

What is AI?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, particularly computer systems, capable of learning, reasoning, analysing, and making predictions. With the ability to process vast amounts of structured and unstructured data, AI excels in data mining, pattern recognition, and predictive modelling. These tools reveal hidden patterns, relationships, and insights that may be difficult or impossible for humans to detect without aid. AI supports:
-
Diagnostics are enhanced by analysing patient features, such as tongue images, pulse waveforms, and symptom profiles, which assists in syndrome differentiation and improves diagnostic consistency.
-
Research by mining historical and modern literature, mapping multi-compound, multi-target mechanisms, and accelerating drug discovery through network pharmacology and chemical data analysis.
-
Clinical Applications through intelligent recommendation systems that personalise acupuncture point selection, herbal prescriptions, and treatment plans, tailored to individual patient needs and constitution.
In Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), AI holds transformative potential by enhancing precision, objectivity, and personalisation in diagnosis, research, and treatment. AI enables the quantification and modelling of TCM’s traditionally experiential practices, revealing the complex interactions and therapeutic pathways of herbal formulations and acupuncture treatments. By synthesising knowledge across eras and modalities, AI empowers a new era of evidence-based, integrative, and globally accessible Chinese medicine, while honouring its holistic foundations.

Artificial Intelligence
Representational Learning
Supports the construction of TCM knowledge graphs, improving the organisation, retrieval, and application of vast amounts of TCM data.
Transfer Learning
Enhances the identification and classification of herbs by applying learned patterns from related tasks to new, data-sparse environments.
Knowledge Structuring and Transfer Learning


Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Generative Pretrained Transformers (GPT)
Extract pharmacological and chemical insights from classical texts and modern TCM literature, transforming unstructured textual knowledge into machine-readable formats for AI analysis.
Language and Text-Based Models
Transformers, originally designed for natural language processing, are now used in TCM for sequential data analysis, such as symptom progression and treatment history. These models are being implemented to recommend inpatient TCM prescriptions in hospital settings, improving the efficiency and consistency of clinical decision-making.
Transformer-Based Models
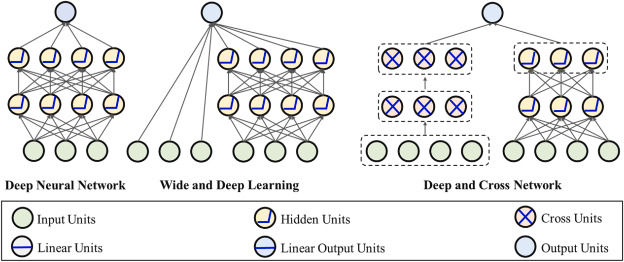
Deep Crossing Networks are designed to process sparse and high-dimensional categorical data, such as patient demographics, symptom types, and TCM pattern classifications. By modelling the complex interactions among these variables, they generate more accurate and personalised prescription recommendations, improving clinical outcomes.