
Common Bloodletting Points
Jingwell points
Classical emergency and Heat-clearing points. Often pricked to release a few drops of blood.
LU11
Acute sore throat, tonsillitis, febrile disease, asthma
LI1
High fever, toothache, sore throat, Wind-Heat
PC9
Fever, coma, mental disturbance
HT9
Heart Fire, mania, palpitations
SI1
Breast abscess, insufficient lactation
SJ1
Febrile illness, red eyes, headache
SP1
Uterine bleeding, insomnia, mental restlessness
LiV1
Hernia, genital swelling, clearing Liver Fire
ST45
Abdominal pain, mania, excessive dreaming
Kid1
Revives consciousness, clears empty Heat
Points for Clearing Heat & Toxicity
Ear Apex (Er Jian)
Hypertension, red eyes, headache, acute fever
GV14
Fever, Heat in Blood, Wind-Heat attack
BL40
Urticaria, eczema, low back pain from Blood Heat
SP10
Blood Heat, skin eruptions, irregular menstruation
Points for Blood Stasis & Pain Relief
Taiyang
Migraine, temporal pain, eye strain
LI11
Inflammation, eczema, red skin lesions
Ashi Points
Pain due to trauma, bruising, stagnation
Points for Skin Disorders & Damp-Heat
BL13-BL17
Chronic eczema, itching, allergic conditions
BL40
Eczema, carbuncles, Blood Heat skin lesions

Common Conditions Treated
Acute sore throat
Clear Heat at LU11, LI1
High fever, delirium
Disperse toxic Heat from DU14, jing-well points
Headache / Hypertension
Reduce Liver Fire via bleeding at Taiyang, GB20, ear apex
Boils / abscesses
Expel Heat and toxins locally
Traumatic injury with stasis
Break up stagnation, reduce swelling
Menstrual blood stasis
Invigorate Blood at SP10, BL17
Urticaria or eczema
Disperse Heat and Wind via plum blossom bleeding
Stroke (acute stage)
Reduce Wind and Fire using jing-well point bleeding
Tapping the skin with a 5- or 7-star needle set (light tapping until slight bleeding). Often used over larger surfaces (e.g. back, chest)
Indications
Chronic skin conditions, Bi syndrome, Heat and Damp accumulation
Plum Blossom Needling with Bleeding
(梅花针放血)
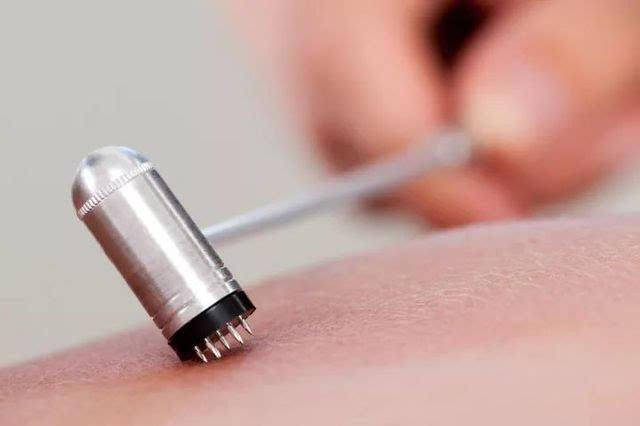

Combine bloodletting with cupping. After pricking or tapping the skin, a cup is applied to draw out blood.
Indications
Toxic Heat, boils, acne, Blood stasis
Wet Cupping
(刺络拔罐)
Shallow needling or lancet pricking of a specific point (e.g. tip of finger, ear, or acupuncture point). Releases a few drops of blood
Indications
Heat in meridians, acute pain, sore throat, headache
Pricking / Spot Bleeding
(点刺放血)


Puncturing visible or engorged veins with a triangle or lancet needle. More blood is released (compared to spot pricking)
Indications
Trauma, Blood stasis, abscesses, local swelling
Needle Bloodletting (刺络放血)
What is Bloodletting?
Bloodletting (in TCM: 刺络疗法, cì luò liáo fǎ or 点刺放血, diǎn cì fàng xuè), also called bleeding therapy, is a traditional technique in Chinese medicine that involves releasing a small amount of blood from the body at specific points to:
-
Eliminate Heat and toxins.
-
Invigorate Blood circulation.
-
Resolve Blood stasis.
-
Clear meridian blockages
-
Reduce swelling and inflammation.
It is an external therapy often combined with cupping, acupuncture, or moxibustion, particularly in Excess or Heat patterns involving Blood stagnation, toxins, or febrile conditions.
Bloodletting Action
Blood Stasis
Invigorates Blood, removes stagnation
Heat in Blood
Cools the Blood, eliminates pathogenic Heat
Toxic Fire
Expels pathogenic toxins through the Blood
Qi and Blood blockage
Opens channels and collaterals, promotes healing

Bloodletting

Precautions and Contraindications
Avoid bloodletting in:
Weak or anaemic patients: May aggravate deficiency
Pregnancy" Can disturb foetus
Bleeding disorders (e.g. haemophilia): Risk of uncontrolled bleeding
Low blood pressure / collapse: May worsen hypotension
Exhausted or elderly with Qi collapse:: Requires tonification, not dispersion
On arteries or deep veins: Dangerous locations
Always use sterile, single-use lancets or needles, apply pressure to stop bleeding, and disinfect the area before and after.