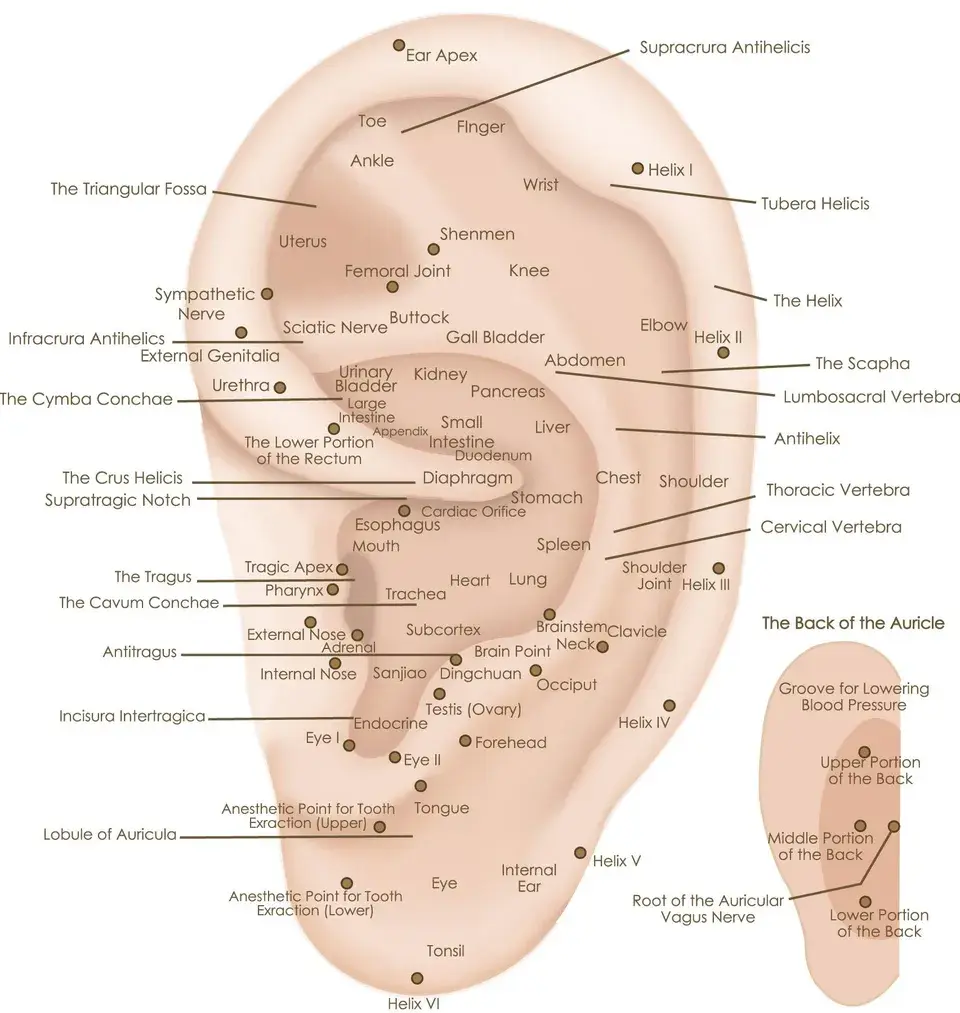
Auricular Bloodletting
(Ear Apex Bleeding)
Light pricking or lancet bleeding at the ear apex (Er Jian)
Indications
Acute hypertension, Fever, Red eyes, inflammation, Migraine
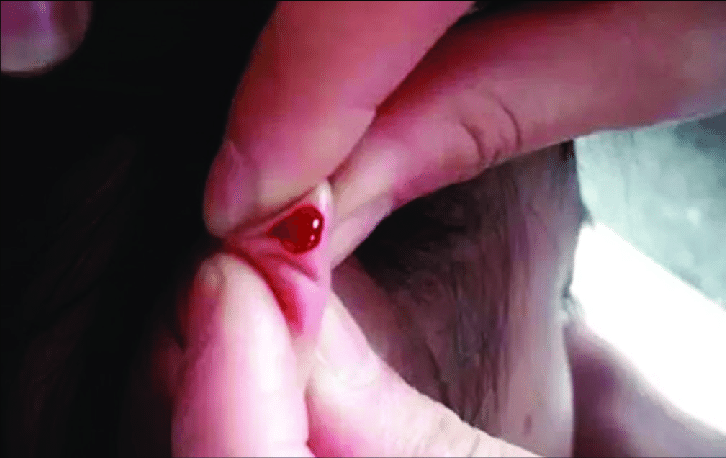
Low-level laser used as a needle-free option.
Method
Use of low-level laser (cold laser) directed at auricular points. No skin penetration, painless, safe for children or sensitive patients
Indications
Pediatric cases, Pain, dermatological condition, Smoking cessation, stress management.
Laser Stimulation (Laser Auriculotherapy)
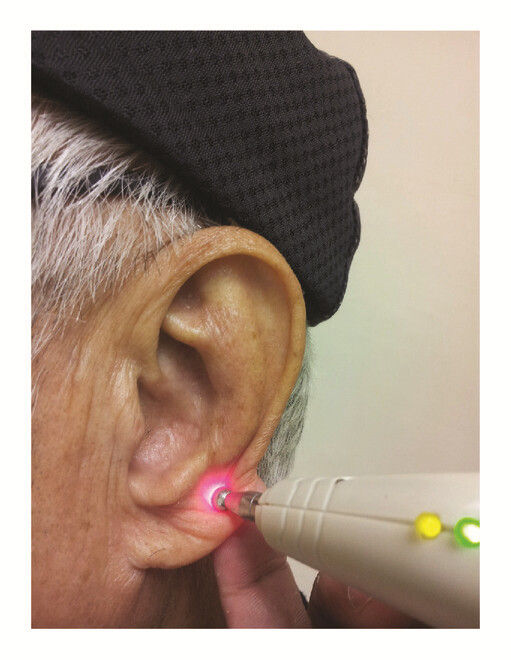

Manual stimulation with finger or probe
Method
Pressing or rubbing auricular points using fingertips, auricular probes, cotton swabs
Indications
Early-stage conditions, Relaxation and self-care, Auricular diagnosis (detecting tender areas)
Manual Pressure (Acupressure / Massage)
Semi-permanent needles fixed for prolonged stimulation
Method
Use of very small semi-permanent needles affixed with tape for prolonged stimulation (1–5 days)
Indications
Smoking cessation, Chronic insomnia, Pain management, Mental health support
Ear Tacks (Embedded Needles)


Low frequency microcurrent applied to selected auricular points
Method
Application of low-frequency electrical current to auricular points using clips or probes
1–100 Hz depending on need, typically used for short durations (5–15 minutes)
Indications
Pain control (especially chronic), Neurological disorders, Stroke recovery, Detox protocols
Electrostimulation (Electro-auriculotherapy)
Insertion of very thin needles into auricular points
Method
Insertion of very fine, sterile needles into specific auricular points (0.5–1.5 mm depth).
Retention Time
20–30 minutes per session
Technique
Tonify (gentle insertion) or sedate (stimulating with rotation) depending on pattern
Indications
Tonify (gentle insertion) or sedate (stimulating with rotation) depending on pattern
Ear Acupuncture

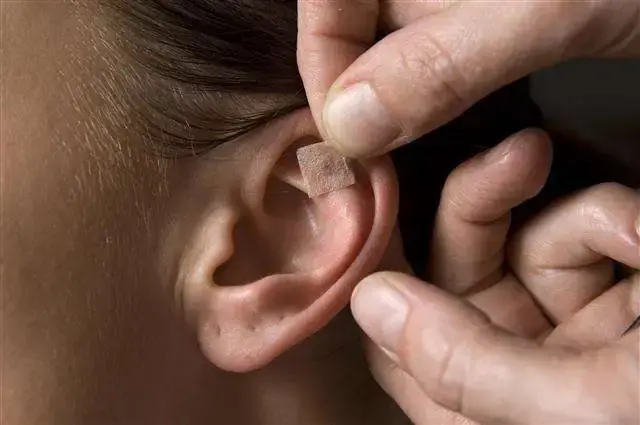
Tiny seeds (e.g. Vaccaria), magnets, or stainless-steel beads taped to points
Method
Application of small seeds (usually Vaccaria seeds), metal beads, or magnetic pellets on adhesive tape, pressed onto specific auricular points
Retention Time
Seeds are usually left in place for 2–5 days
Indications
Chronic conditions, Pediatric or needle-sensitive patients, Stress, weight loss, PMS, migraines
Ear Seeds
(Auricular Press Pellets)
Auricular Therapy
Auricular therapy (耳针疗法, ěr zhēn liáo fǎ), also known as auriculotherapy or ear acupuncture, is a diagnostic and therapeutic system based on the stimulation of specific points on the external ear to treat diseases and dysfunctions throughout the body. In Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), the ear is considered a microsystem that reflects the entire body, much like reflexology in the feet or palm diagnosis in the hands. Stimulating specific points on the auricle can regulate Zang-Fu organ function, Qi and Blood circulation, and emotional states. Core Principles of Auricular Therapy in TCM:
Microsystem Theory: The ear represents an inverted foetus: Lobe → head and face, Scapha → upper limbs, Antihelix → trunk and spine, Cavum conchae → internal organs and helix → lower limbs.
Qi and Blood Connection: All 12 regular meridians and eight extraordinary vessels connect to the ear through the Small Intestine, Gallbladder, Sanjiao, and Heart channels.
TCM Diagnosis via the Ear: Changes in colour, texture, temperature, pain sensitivity, or electrical conductivity at certain ear zones can reflect internal disharmony.

Auricular Therapy

Common Auricular Zones
In auricular therapy, the external ear (auricle) is considered a microsystem that reflects the entire body — similar to a hologram. Each region of the ear corresponds to a specific anatomical area, organ, or function, based on the concept of an inverted foetus mapped onto the auricle. This model is the foundation of auricular therapy:
-
Ear lobe → Head and facial region (brain, eyes, jaw, teeth)
-
Antihelix → Spine and trunk
-
Scapha → Upper limbs (shoulder, elbow, wrist)
-
Helix → Lower limbs
-
Cavum and cymba conchae → Internal organs
-
Tragus and antitragus → Brain and neuroendocrine areas
Ear Lobe
Head and Face Region
This is the "head" of the inverted foetus. It contains facial and sensory organ points
Lower part of the ear (lobule), subdivided into anterior and posterior zones.
Eye
Vision, inflammation
Inner ear
Hearing, vertigo
External Ear
Otitis, tinnitus
Tongue
Speech, taste
Teeth / Jaw
Toothache, TMJ
Brain
Mental Clarity, memory
Tragus / Antitragus
Brain & Nervous System
This area governs the central nervous system, endocrine, and autonomic regulation
Anterior inner fold (tragus) and posterior protrusion (antitragus).
Subcortex
Sleep, anxiety, epilepsy
Brainstem
Neurological issues
Thalamus
Pain control, sensory integration
Endocrine
Hormonal regulation, menopause
Adrenal
Stress, fatigue
Pituitary
Growth, hormone axis
Cavum Conchae
Thoracic Organs
This inner bowl of the ear corresponds to organs of the chest
Lower inner cavity of the auricle (concha below the crus of the helix).
Lung
Asthma, cough, immunity
Heart
Palpitations, anxiety
Trachea
Bronchitis, sore throat
Oesophagus
Acid reflux, digestion
Cymba Conchae
Abdominal Organs
This upper bowl of the concha relates to abdominal organs
Upper inner cavity of auricle above the crus of the helix.
Liver
Emotions, detox, PMS
Gallbladder
Bile regulation, tension, migraines
Kidney
Lower back pain, fertility, fatigue
Stomach
Digestion, nausea, appetite
Pancreas/ duodenum
Diabetes, metabolism
Spleen
Dampness, fatigue, digestion
Small Intestine
Absorption, diarrhoea
Large Intestine
Constipation, bowel regulation
Antihelix
Spine and Trunk
The Y-shaped ridge inside the ear represents the spinal column and torso
From bottom to top of antihelix → lumbar → thoracic → cervical
Cervical Vertebrae
Neck pain, stiffness
Thoracic Vertebrae
Upper/mid back pain
Lumbar Vertebrae
Low back pain, sciatica
Sacrum
Pelvic pain, menstruation
Chest/Abdomen
Digestive and respiratory aid
Scapha
Upper Limbs
Outer fold between the helix and antihelix, representing arms and hands
Narrow groove wrapping from top of ear toward antihelix
Shoulder
Shoulder pain, tension
Elbow
Tennis Elbow
Wrist/Hand
Carpal tunnel, arthritis
Helix
Lower Limbs and Skin
The outermost rim of the ear corresponds to legs and skin-related issues
Around outer edge from bottoms up to apex
Hip
Sciatica, hip pain
Knee
Arthritis, mobility issues
Ankle/Foot
Gait, balance, circulation
Allergy Point
Skin disorders, immunity
Triangular Fossa
Shen and Hormonal Points
Upper notch area in front of antihelix, key for emotional and hormonal
Small triangle-shaped zone above the cymba conchae
Shen Men
Calms the mind, sleep, stress
Ovary
Menstruation, fertility
Uterus
Gynaecology, PMS, cramps
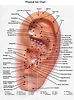
Common Used Auricular Points
Apex of the triangular fossa
Calms the Shen (mind); Relieves stress, anxiety, insomnia; Reduces pain sensitivity; Central point in NADA protocol (addiction detox)
Sympathetic (交感) – Autonomic Point
Junction of the inferior antihelix crus and cavum conchae
Regulates the autonomic nervous system; Relieves pain, spasms, and inflammation; Used for digestive disorders, hypertension, and stress
Cavum conchae, near the heart and trachea points
Regulates breathing, treats asthma, cough, bronchitis; Clears skin disorders; Emotional regulation of grief and sadness.
Centre of the cavum conchae
Treats palpitations, tachycardia, calms mental restlessness, insomnia, anxiety, Used in cardiac disorders
Cymba conchae, upper region
Regulates Liver Qi: useful in irritability, depression; Treats menstrual issues, PMS; Detoxifies, supports vision and digestion
Close to the Stomach point, anterior cymba conchae
Regulates digestion, transformation, and Dampness; Boosts immune function; Useful in fatigue, edema, diarrhea
Base of the intertragic notch
Balances hormones, used in menstrual irregularities, diabetes, thyroid disorders, Regulates endocrine system
Centre of the concha, intersection of horizontal and vertical ear axes
Restores homeostasis (Yin-Yang balance), Normalizes endocrine, nervous, and organ function, Used as a grounding balancing point in most protocols
Inside inferior tragus
Anti-inflammatory, anti-allergy; Regulates stress response, useful in fatigue, hypotension
Medial side of antihelix, near triangular fossa
Regulates menstrual cycles, Treats infertility, PMS, menstrual cramps, Supports hormonal balance
Cymba conchae, lower posterior area
Tonifies Kidney Qi and Essence; Supports low back pain, hearing loss, urination; Used in fertility and hormonal protocols
Inferior cymba conchae, below the helix crus
Regulates appetite, digestion, nausea, and vomiting; Used in weight loss protocols; Treats gastritis, acid reflux
Inner wall of antitragus
Controls cerebral cortex activity, Treats pain, epilepsy, insomnia, often paired with Shen Men for psychological disorders